 Inductive Modem Module
Inductive Modem ModuleIMM
 Inductive Modem Module
Inductive Modem Module![]()
![]() Print version
Technical Reference Manual -
Current (older)
Configuration options & accessories
Print version
Technical Reference Manual -
Current (older)
Configuration options & accessories
Description
Inductive modem telemetry is a proven technology for real-time communication between underwater devices and moored buoys. Early inductive modem systems were instrument-specific and highly constrained. The Inductive Modem Module (IMM) sets a new standard for inductive modem telemetry and opens the door to a new generation of compact, low-power devices for real-time applications. The IMM is designed to interface with existing devices or to be placed as a component on printed circuit boards in new instruments, such as the SBE 37-IMP, 39-IM, and a growing selection of moored instruments made by other manufacturers
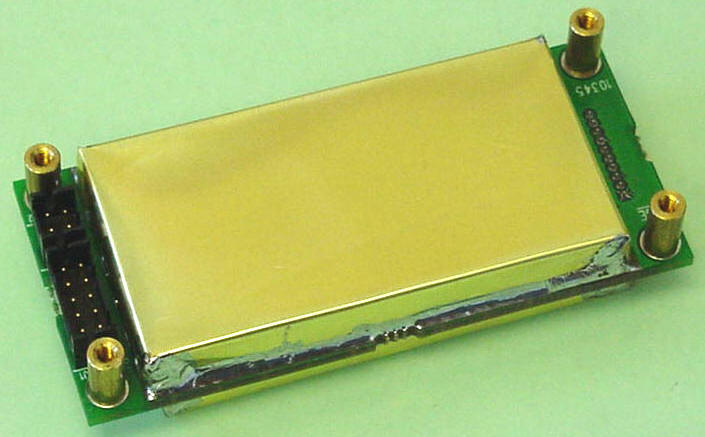


Size: 3.1 x 7 x 1.6 cm (1.2 x 2.8 x 0.6 inches)
Note: Photos above show IMM with electrical pins on the
bottom, configured to plug into electrical connection below it. IMM can also be
configured with the pins oriented for a connection at the side; see drawing 41453
for details.
 SUMMARY
SUMMARY
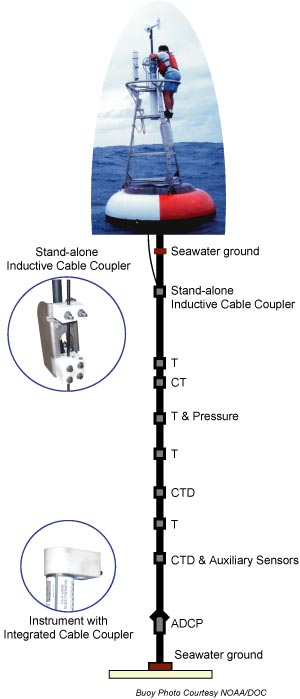
INDUCTIVE MODEM (IM) BASICS
Inductive modems allow communication with underwater instruments in real time, on moorings using plastic-jacketed wire rope as all or part of the load-bearing mooring line. The wire rope, in contact with seawater at each end, conducts electrical signals in a loop, where seawater is the electrical return path. IM devices couple to this loop inductively along the insulated (jacketed wire) part of this loop without direct electrical connection. The coupling is achieved using a toroid transformer in which the mooring wire and seawater return form a single winding. Since there is only one current path, only one device can transmit at a time (half-duplex). Sea-Bird inductive modems are integral components in the TAO/TRITON array, RAPID/MOCHA moorings, and most other real-time ocean mooring systems.
ADVANCED FEATURES
The IMM includes advanced features to assist existing techniques and support development of the next generation of mooring systems:
Output Tags
The IMM uses markup tags to pass data to the Host in a structured format. Markup tags are key words that identify the associated data. The similarity to XML is a convenience for data output only; the IMM does not require XML input. The markup tags allow a more structured approach to data processing without compromising traditional methods. IMM Output Tags and Data Tags should not be treated as XML unless the user-settable data follows the rules of XML. The IMM does not force XML compliance on users.
Host ID String
The Host ID is a user-settable 64-character string stored in the IMM's persistent memory. It provides a means of identifying the instrument connected to the IMM without interacting with the instrument itself.
Host Data File
The Host Data File is a general-purpose 4 Kbyte persistent memory space in the IMM reserved for application-specific information. This might store data describing the host instrument, binary code for host data processing, XML data, the Host command set, or network-specific interface data. The Host Data File can be uploaded through the IM interface.
Serial Number Addressing
Previous IM systems used user-programmed device IDs to address instruments on the network. If two devices were accidentally deployed with the same ID, neither instrument would communicate properly. The IMM solves this problem with optional Serial Number Addressing. Commands may be addressed to a specific IMM's 8-digit decimal serial number. IMM serial numbers are programmed at the factory and cannot be modified.
Group Command Addressing
Group commands allow addressing of pre-defined logical groups of instruments. For example, it may be useful to place all SBE 39-IM temperature recorders in Group 1, all SBE 37-IMP MicroCATs in Group 2, etc. allowing you to set / reset parameters in all similar instruments at the same time. A maximum of 9 groups may be defined per mooring.
Discovery
Discovery is the automated process of identifying devices connected on an IM network. This allows recovery from deployment or configuration errors and has considerable potential in more complex self-configuring systems. The host starts the discovery process with the DISC command. The IMM responds in seconds with a list of serial numbers of IMMs detected on the network.
Sample Data Memory
Sample Data is a 16 Kbyte persistent memory space reserved for passing data from IMM-equipped instruments to data collectors or buoy controllers. The Sample Data structure is limited to 40 stored samples. Sample Data provides a level of independence between devices collecting the data and devices recording the data. Each new instrument may be programmed to write data to the IMM's Sample Data structure. The buoy controller periodically checks IMMs for new samples, uploads data, and clears successfully uploaded samples. The buoy controller may tag the data with the Host ID stored in the IMM. This allows the buoy controller to use the same code to upload data from any IMM-equipped instrument.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION / LINKS:
Documentation -- manual, photos, technical papers, application notes
Sales Information -- options, accessories, cables, mount kits, spares, etc.
Links to Other Instruments of Interest
![]()
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Sea-Bird Home Phone: (+1) 425-643-9866 E-mail: seabird@seabird.com